Proteins with calmodulin-like domains: structures and functional roles | Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences

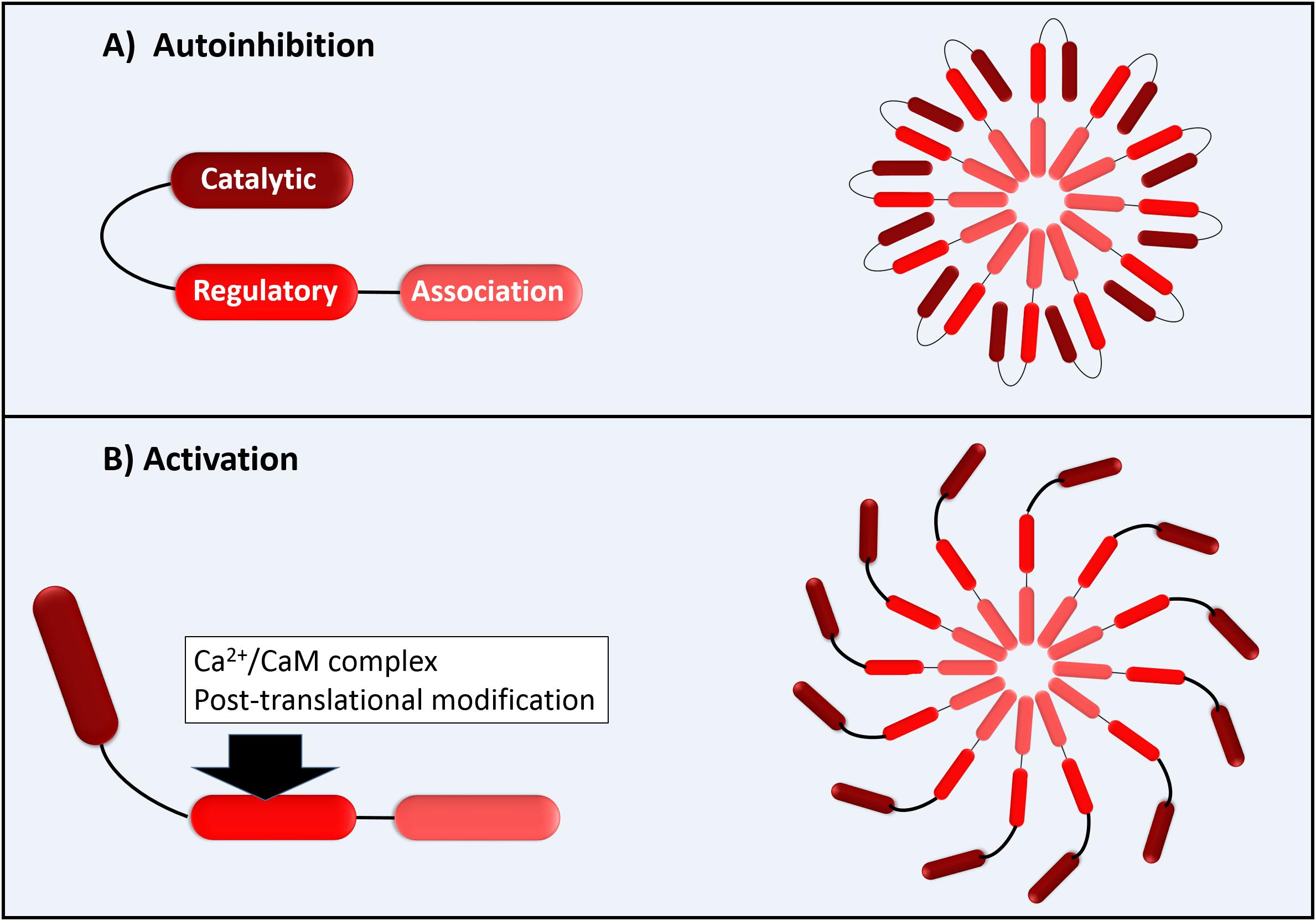
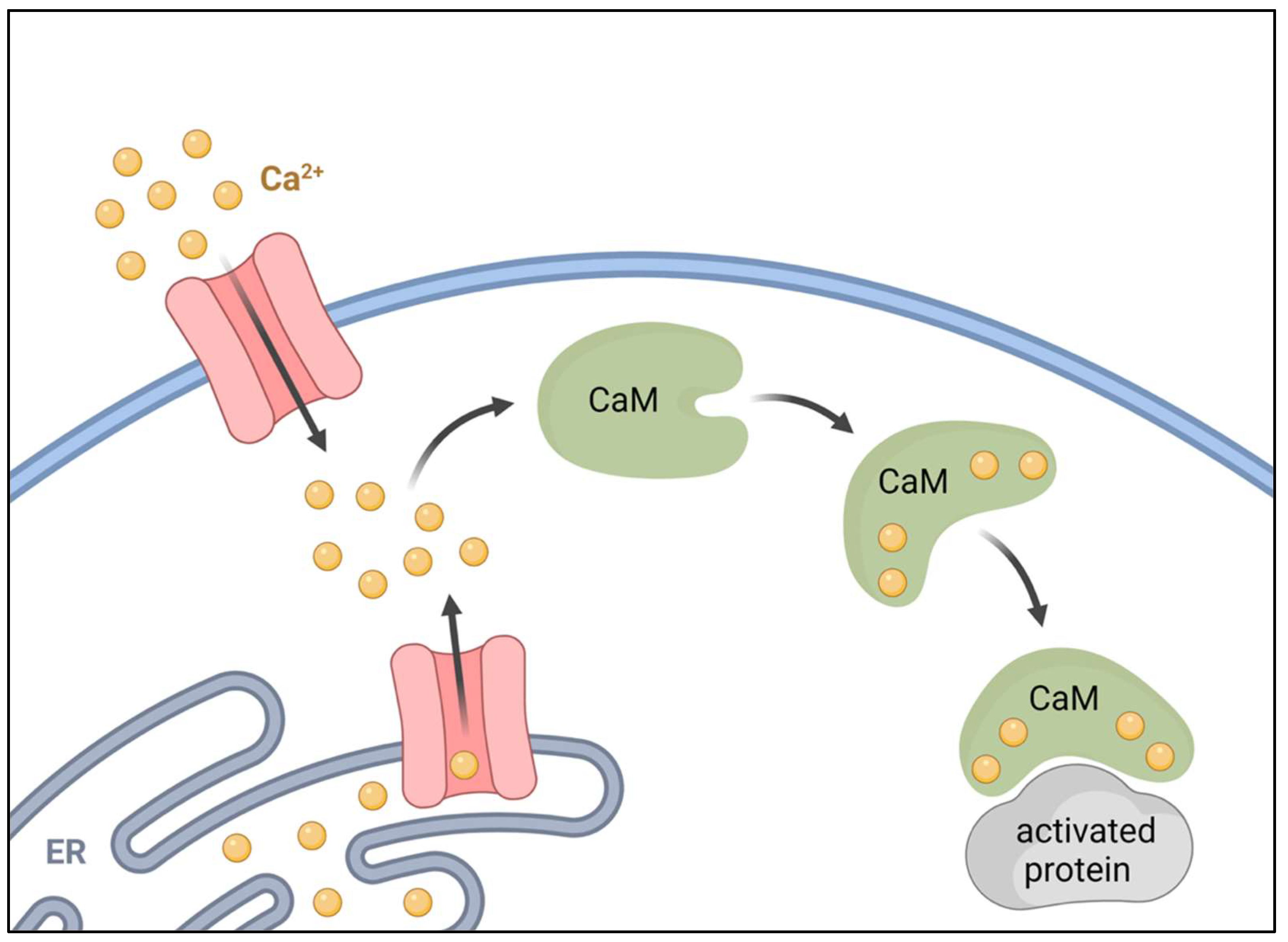
The Ca 2+ -dependent activation of Ca 2+ /Calmodulin (CaM)-dependent... | Download Scientific Diagram

Figure 5. | Bidirectional Regulation of Cytoplasmic Polyadenylation Element-Binding Protein Phosphorylation by Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II and Protein Phosphatase 1 during Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation | Journal of Neuroscience

Three dimensional structure of CaM protein. (I) Secondary structure of... | Download Scientific Diagram
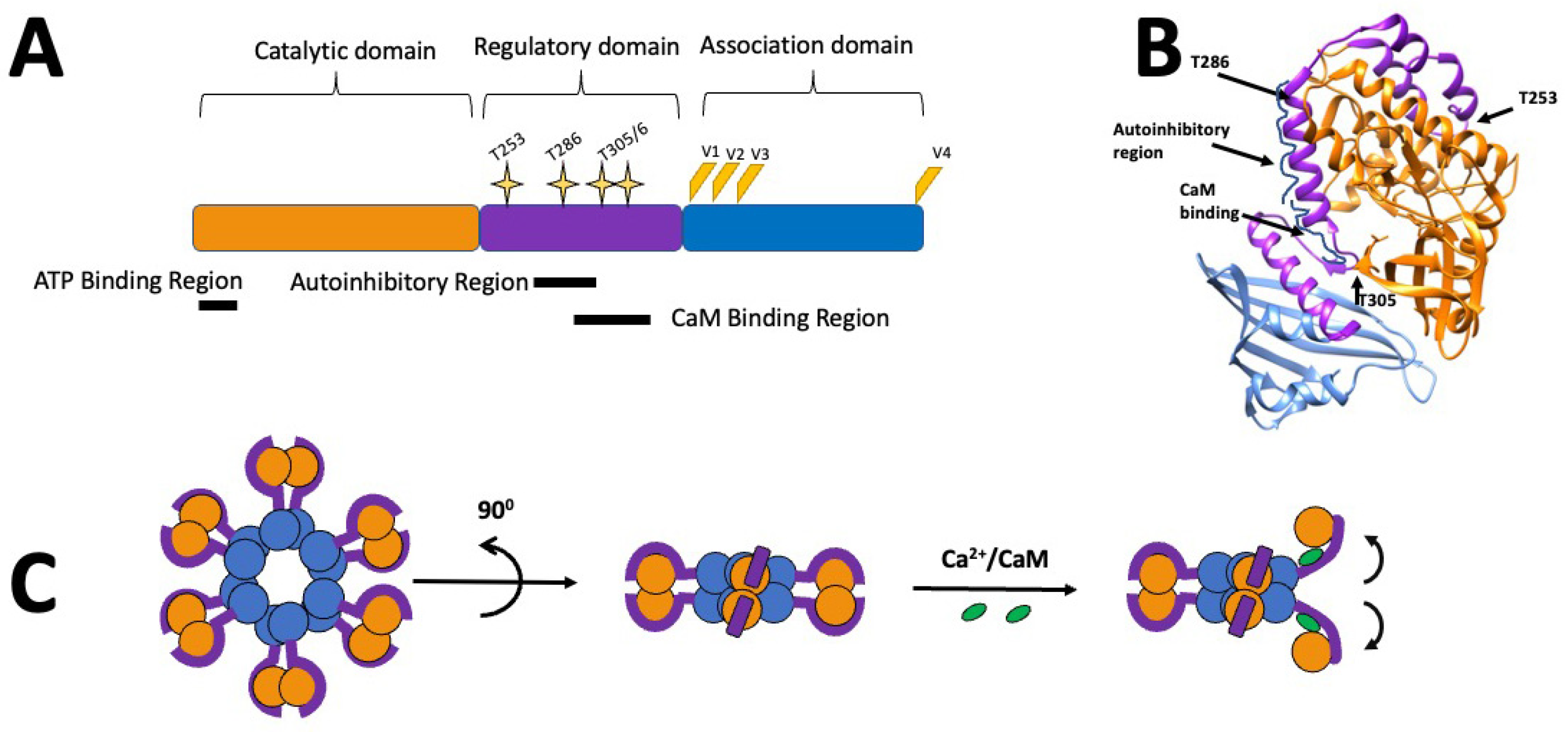
Frontiers | An Overview of the Role of Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase in Cardiorenal Syndrome
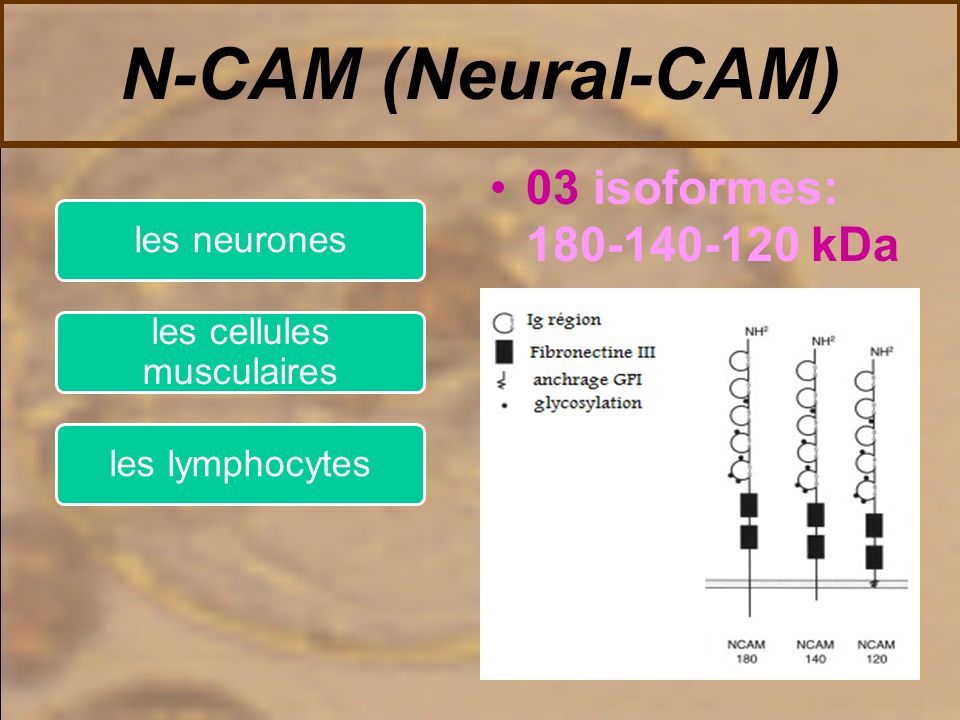
Protéines d'adhésion. Les CAMs Les molécules d'adhérence cellulaire des glycoprotéines transmembranaires Leurs propriétés adhésives dépend ou non. - ppt télécharger
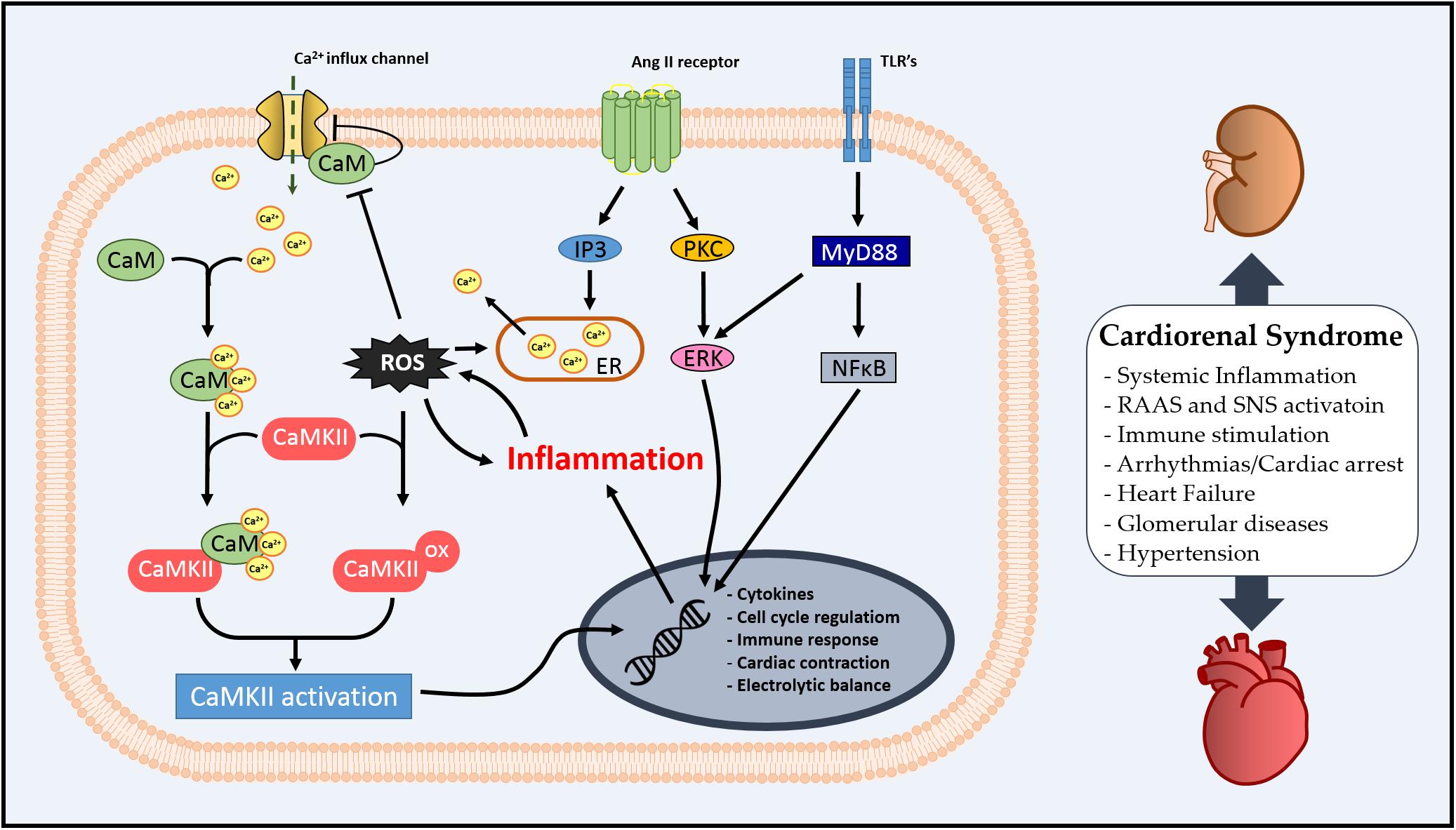
Frontiers | An Overview of the Role of Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase in Cardiorenal Syndrome

Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) regulate protein synthesis machinery.... | Download Scientific Diagram

Eurofins DiscoverX CaM Kinase IIγ Protein, Active Quantity: 250 μg Eurofins DiscoverX CaM Kinase IIγ Protein, Active | Fisher Scientific

Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) regulate protein synthesis machinery.... | Download Scientific Diagram

Proteins with calmodulin-like domains: structures and functional roles | Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Calcium Signalling in Heart and Vessels: Role of Calmodulin and Downstream Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinases

CaM-like modelled protein with its ligand IQ1 motif. (a) Superimposed... | Download Scientific Diagram

The KN-93 Molecule Inhibits Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II (CaMKII) Activity by Binding to Ca2+/CaM - ScienceDirect
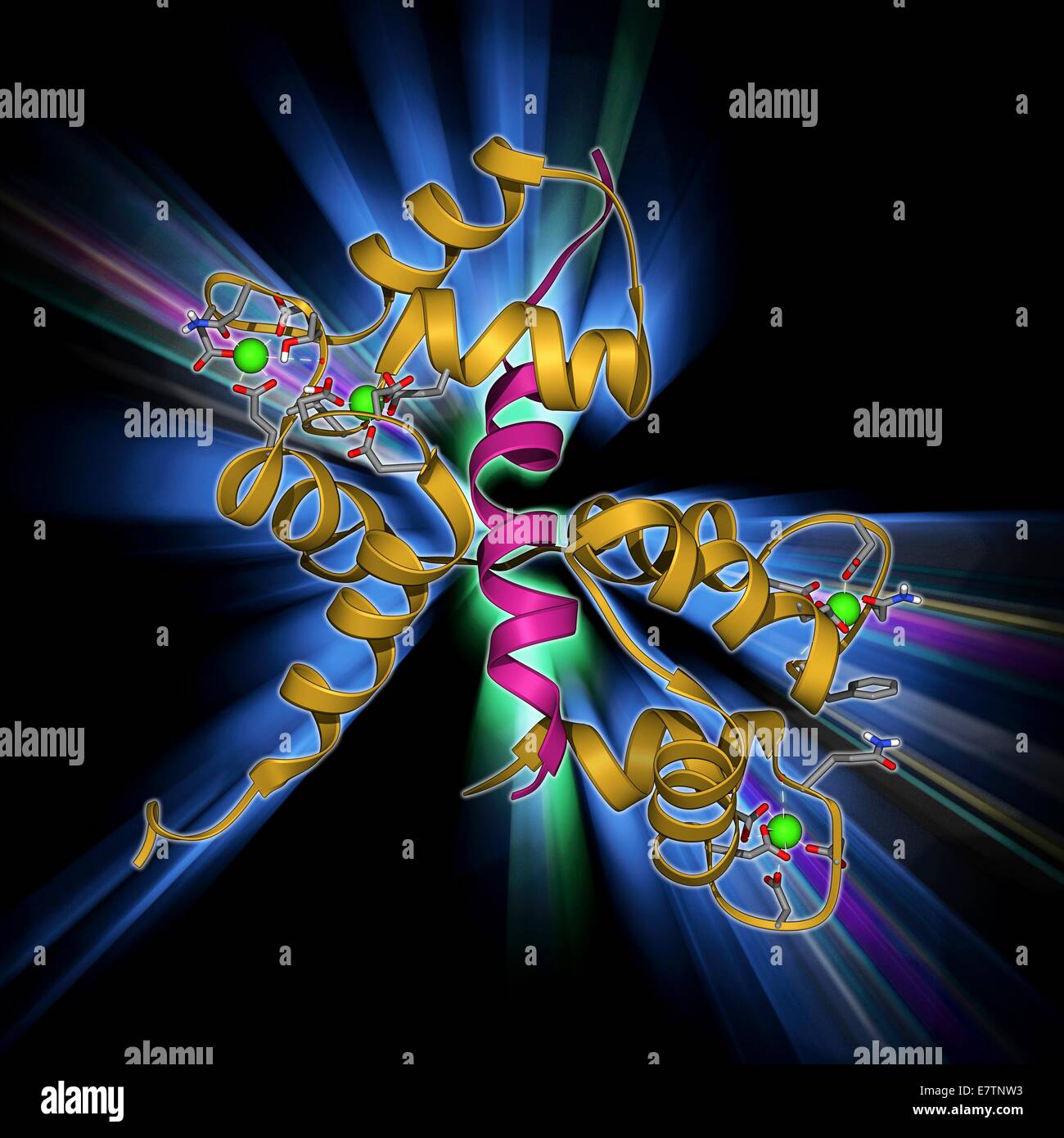
Protéines liant le calcium. Molécule modèle de la protéine liant le calcium, la calmoduline (CaM) lié à une kinase de la chaîne légère de la myosine-molécule. Ce complexe est impliqué dans la